A 14 yo male with pain in calcaneum since 1months.
MRI foot for calcaneum with CT correlation shows:
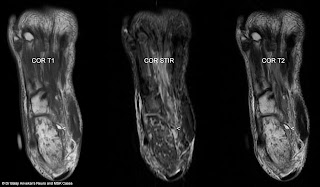
Heterogeneous signal abnormality diffusely involving calcaneum with multiple low signal intensity foci diffusely scattered in calcaneum on T1-weighted images which are hyperintense on STIR. Rest of the intervening calcaneum medulla shows faint high signal on STIR.
No obvious density abnormality on CT. No obvious sclerotic or lytic lesion. No obvious cortical destruction or sclerosis.
There is a focal lentiform shaped parosteal collection measuring approximately 26 mm in height and 6 mm in thickness medially at 2 o’clock position and 4 mm in thickness laterally on plantar aspect at 7 o’clock position on axial section.
There is fat – fluid level within this collection, focal fat in the supernatant portion of this collection which is hyperintense on T1-weighted images with complete signal suppression on STIR, this portion follows classical fat density on CT.
There is an associated diffuse oedema involving muscles of plantar aspect of foot especially quadratus plantae muscle, medial as well as lateral teno synovitis.
This finding suggestive of extramedullary focal fat - fluid level which is a pathognomonic sign of acute to subacute osteomyelitis.
Findings were discussed with the referring physician before finalizing the report, who added that there is elevation of inflammatory markers in lab reports and the suspicion of osteomyelitis clinically as well, with a feedback of significant improvement clinically after IV antibiotics.
Take home note is during MSK MRI interpretation, a bone marrow signal abnormality with an associated focal periosteal extra medullary fat – fluid level, osteomyelitis should be in the list of your differential diagnosis.
References:
1. Extra-osseous fat fluid level: a specific sign for osteomyelitis. Kumar J, Bandhu S, Kumar A, Alam S. Skeletal Radiol. 2007 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S101-4. doi: 10.1007/s00256-006-0194-1. Epub 2006 Sep 19.
2. Intramedullary and extramedullary fat globules on magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic sign for osteomyelitis. Davies AM, Hughes DE, Grimer RJ. Eur Radiol. 2005 Oct;15(10):2194-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-005-2771-4. Epub 2005 Apr 29.