A 50 yo male operated for right parietal Glioma with post operative radiotherapy.
Clinically started worsening after 5th week.
The follow up CT with MRI FLAIR and T2*GRE.
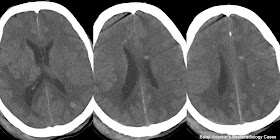 |
| Non Contrast CT study of brain shows multiple punctuate hyperdense foci are the Radiation induced Cryptic Vascular Malformation |
 |
| Axial FLAIR image show bilateral confluent peri ventricular T2 white matter hyper intensities suggestive of Radiation induced Leukoencephalopathy |
Spectrum of insult includes edema, arteritis, leukoencephalopathy, mineralizing microangiopathy, necrotizing leukoencephalopathy, radiation-induced tumors and Cryptic Vascular Malformations.
Depending up on the time of presentation divided into acute, early delayed injury and late delayed injury:
Acute injury: 1-6 weeks after or during treatment ; Mild and reversible, vasogenic edema.
Early delayed injury: 3 weeks to several months; Edema & demyelination.
Late delayed injury: Months to years after treatment; More severe, irreversible.
Imaging findings:
Radiation injury: Mild focal hypodense / T2 hyper intense vasogenic edema to areas of necrosis.
Radiation necrosis: Irregular enhancing lesion, single or multiple.
Leukoencephalopathy: Bilateral confluent white matter hypodensity / T2 hyperintensity predominantly involve peri ventricular white matter, sub cortical U fibers involves late.
Mineralizing microangiopathy: Bilateral basal ganglia and sub cortical white matter faint calcification best seen on CT. An associated cerebral cortical atrophy.
Necrotizing leukoencephalopathy: Areas of white matter necrosis.
Cryptic Vascular Malformation: Best seen on MRI T2* GRE as punctate low signal intensity foci represent capillary Telangiectasia.
Pathological Basis:
Radiation-induced neurotoxicity : Direct radiation induced Glial and WM damage. Sensitivity of oligodendrocytes is more than neurons to radiation induced damage. Effects on fibrinolytic system and immune effects.
Radiation-induced vascular injury: Altered vascular permeability, endothelial and basement membrane damage, accelerated atherosclerosis, telangiectasia and cavernoma formation.
Radiation-induced tumor like sarcoma seen after ~ 5 years, genetic predisposition.
Distinguishing residual/recurrent neoplasm from Radiation induced Necrosis difficult using morphology alone. MRS, PET or SPECT may help delineate recurrent tumour from radiation necrosis.
Reference: DI Anne G Osborn.

Your blog is so interesting and very informative; the quality you used in penning this is excellent. Thanks for posting this.
ReplyDeletewww.n8fan.net